What is Injection Molding Powder Metallurgy?
What is Injection Molding Powder Metallurgy?
The application range of powder metallurgy products is very wide, from ordinary machinery manufacturing to precision instruments; from hardware tools to large machinery; from electronic industry to motor manufacturing; from civil industry to military industry; from general technology to cutting-edge high technology. The figure of powder metallurgy process. The following is the powder metallurgy process flow and the advantages and disadvantages of the process.
Ⅰ.Powder metallurgy process flow
1. Flour making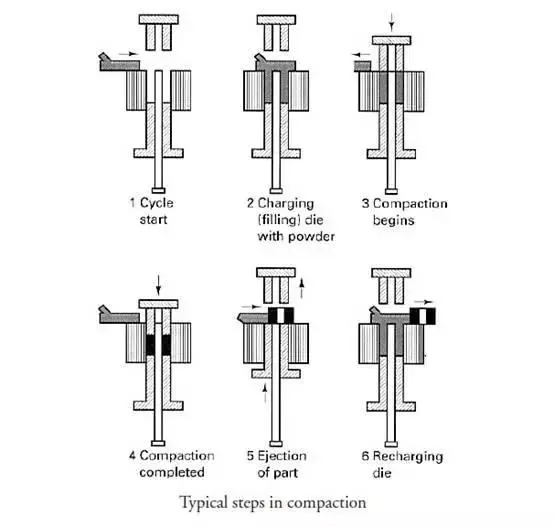
Milling is the process of turning raw materials into powder. Commonly used milling methods include oxide reduction method and mechanical method. or buy directly
2. Mixing
Mixing is the process of mixing various required powders in a certain proportion and homogenizing them to form green powder. There are three types: dry type, semi-dry type and wet type, respectively used for different requirements.
3. Forming
Forming is the process of placing uniformly mixed materials into a die and pressing them into a parison with a certain shape, size and density. Molding methods are basically divided into pressure molding and pressureless molding. The most commonly used type of pressure molding is compression molding.
4. Sintering
Sintering is a key process in the powder metallurgy process. The formed compact is then sintered to obtain the required final physical and mechanical properties. Sintering is divided into unit system sintering and multi-system sintering. In addition to ordinary sintering, there are also special sintering processes such as loose sintering, immersion method, and hot pressing method.
5. Post-processing
Post-sintering treatment can be done in a variety of ways according to different product requirements. Such as finishing, oil immersion, machining, heat treatment and electroplating. In addition, in recent years, some new processes such as rolling and forging have also been used in the processing of powder metallurgy materials after sintering, achieving ideal results.
Ⅱ. Advantages of powder metallurgy process
1. Special materials can be processed. The powder metallurgy method of materials can produce refractory metals as well as compounds, pseudo-alloys, and porous materials.
2. Save metal and reduce costs. Because powder metallurgy can be pressed into final size compacts, no mechanical processing is required. The loss of metal produced using this method is only 1-5%, while general processing will consume 80% of metal.
3. Preparation of high-purity materials. The powder metallurgy process does not melt the material during the material production process, so there will be no impurities brought by other substances. Sintering is carried out in a vacuum and reducing atmosphere, so there is no fear of oxidation and no contamination of the material. Therefore, the purity of the product is relatively high.
4. Correct distribution of materials. The powder metallurgy method can ensure the correctness and uniformity of material composition in proportioning.
5. Mass production reduces costs. Powder metallurgy is suitable for the production of large quantities of products with uniform shapes, such as gears and other high-cost products, which can greatly reduce production costs.
Ⅲ. Disadvantages of powder metallurgy process
1. Powder metallurgy products have poor strength and toughness. Since the internal pores of the compact formed by powder pressing cannot be completely eliminated, the strength and toughness of powder metallurgy products are inferior to those of castings and forgings of corresponding compositions.
2. Powder metallurgy cannot be made into large products. Since the fluidity of metal powder is worse than that of liquid metal, its shape and size will be subject to certain restrictions, and its weight will not exceed 10 kilograms.
3. The cost of stamping molding is relatively high. Since the manufacturing cost of stamping molds is too high, they are only suitable for use in mass production.
Powder injection molding is the product of the infiltration and intersection of plastic molding technology, polymer chemistry, powder metallurgy technology and metal materials science. Metal powder injection molding uses molds to injection mold blanks just like plastic injection molding. However, powder injection molding also requires sintering to quickly manufacture high-density, high-precision, three-dimensional complex-shaped structural parts, and to quickly and accurately materialize design ideas into Products with a certain structure and function, and parts can be directly mass-produced, are a new change in the manufacturing technology industry.






