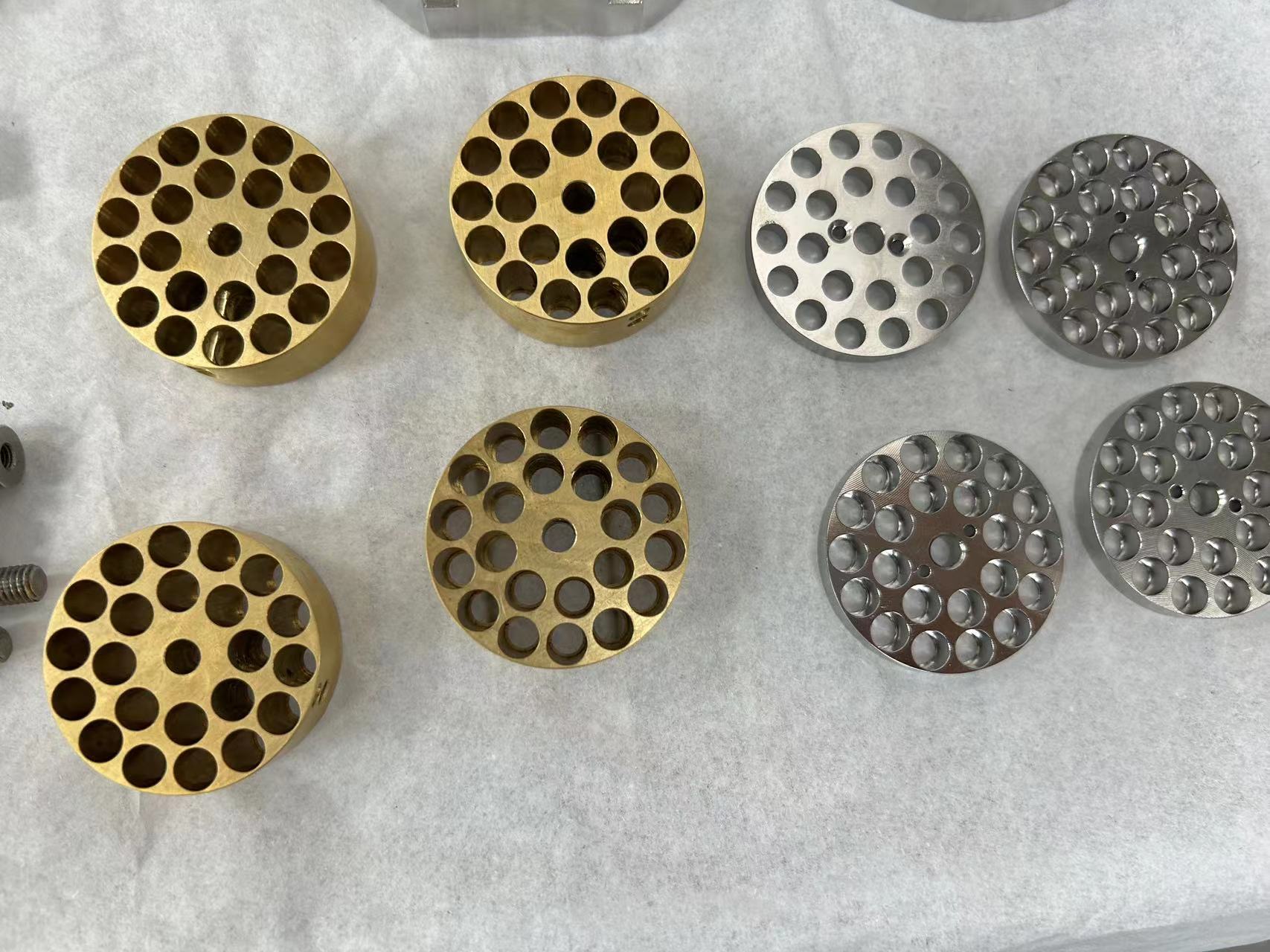
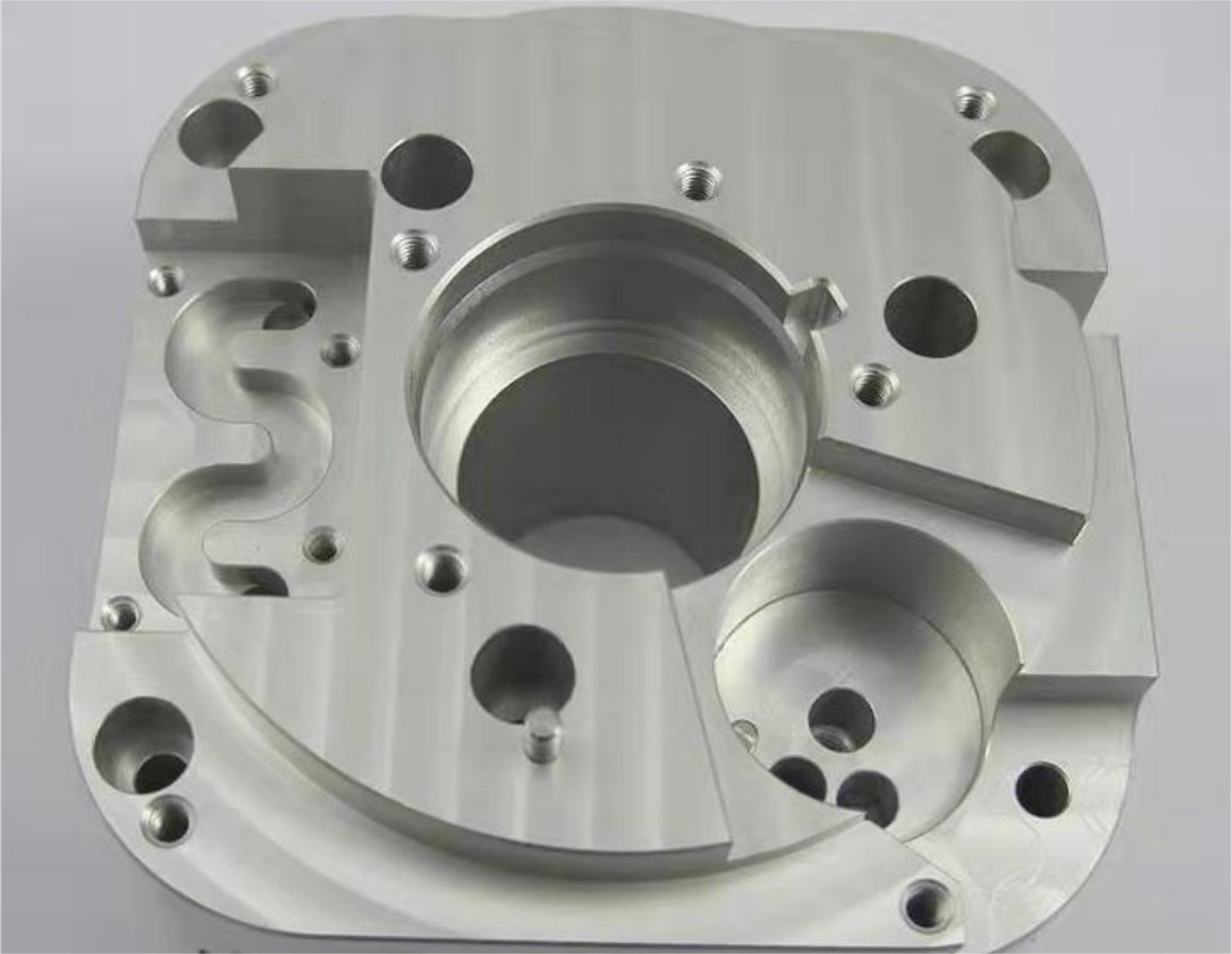
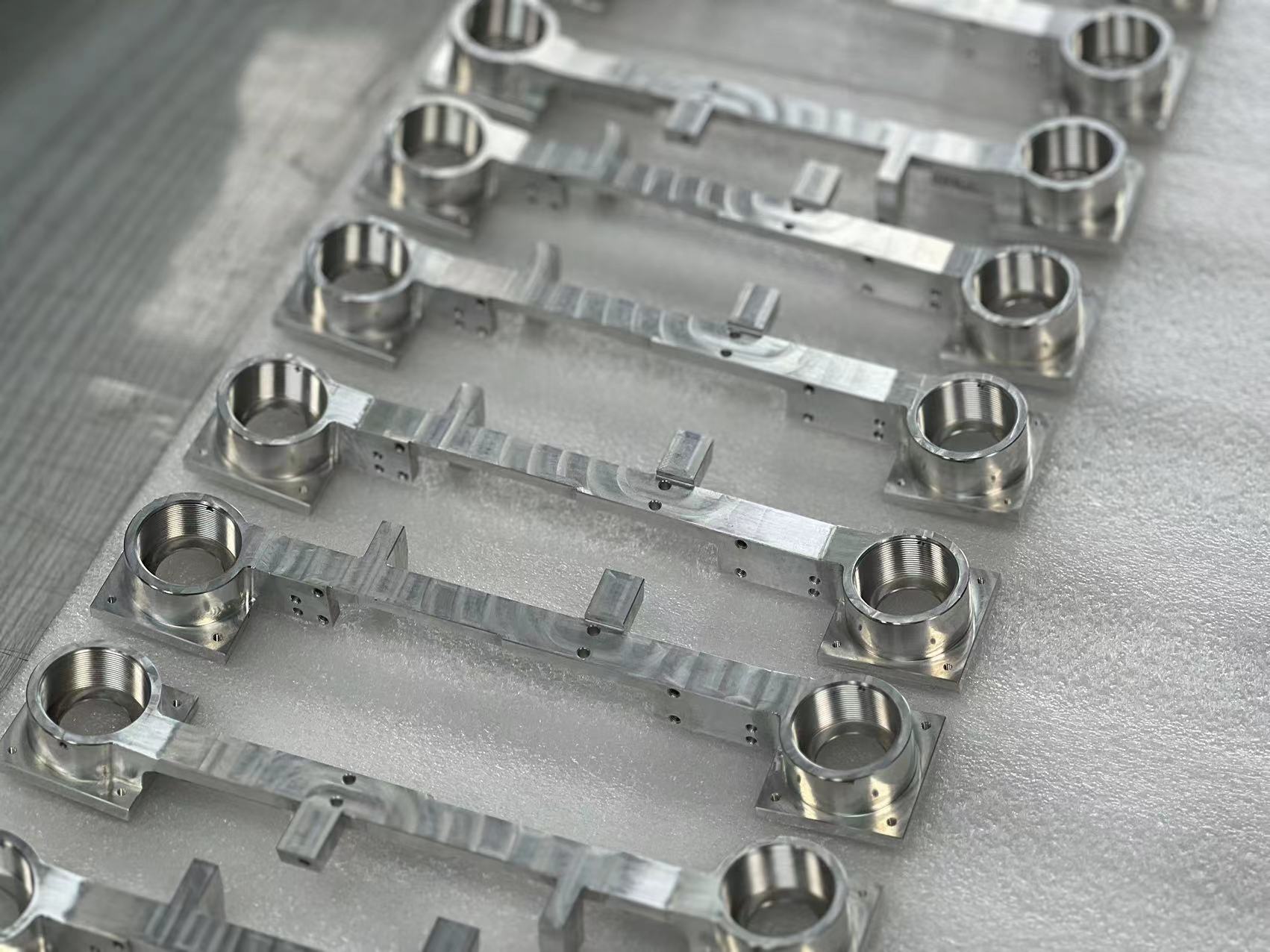
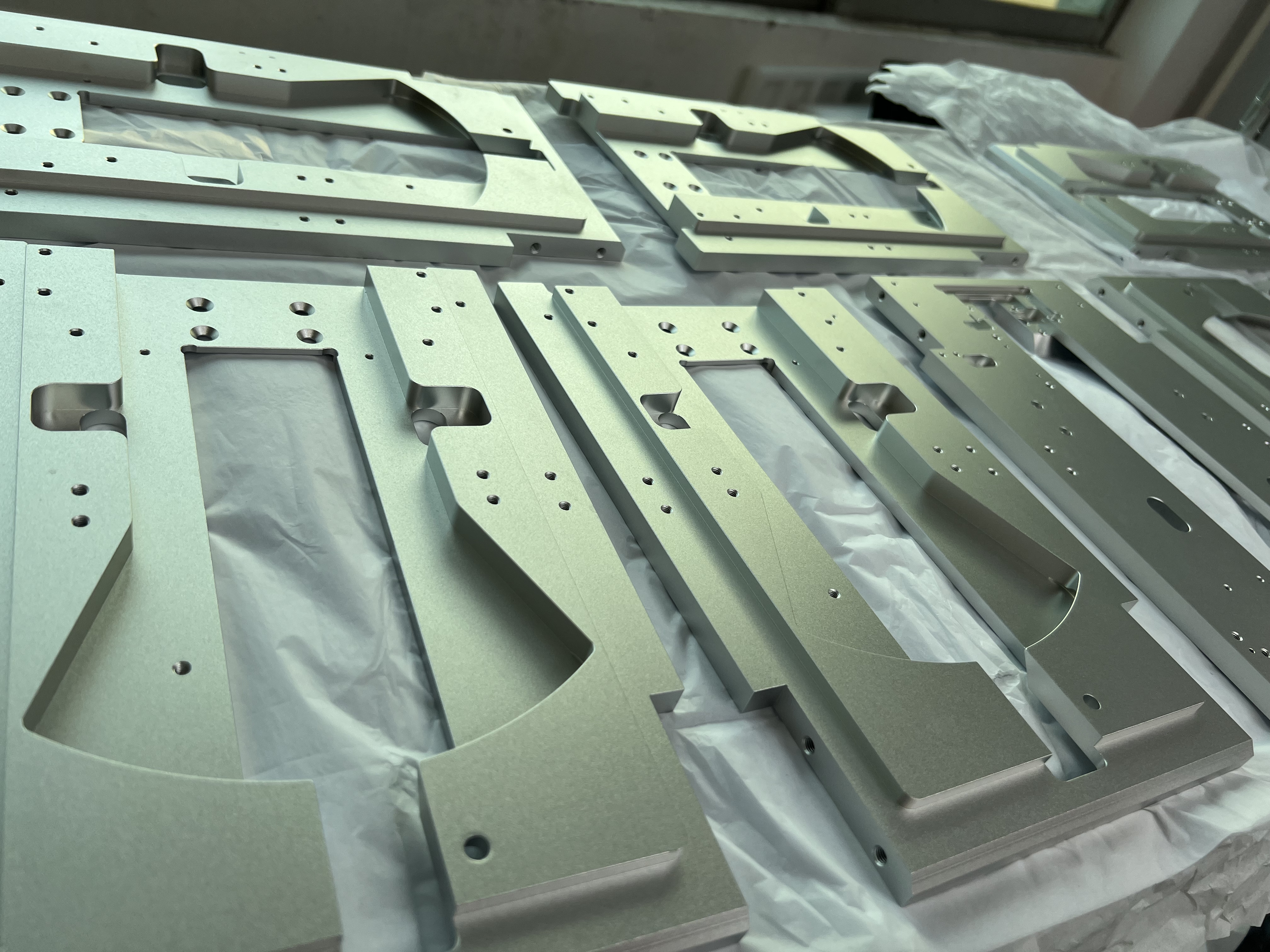
SS316
SS 316 It is the second most widely used steel after 304 and contains 16% to 18% chromium, 11% to 14% nickel and at least 2% molybdenum. These combine to improve corrosion resistance. In particular, molybdenum is used to help control corrosion pitting. This grade can withstand stains in temperatures up to 1600F.
Used in chemical processing, pulp and paper industry, food and beverage and surgical equipment, processing and distribution and corrosive environments. It is also used in the marine industry because it is more resistant to chloride corrosion than 304. SS316 is commonly used in nuclear fuel recovery equipment. Grade 18/10 stainless steel typically meets this application grade.
The strength, hardness, workability grade and temperature resistance of stainless steel 316 are between those of aluminum and titanium. Stainless steel is also generally less expensive than aluminum or titanium alloys and has better weldability.
316 stainless steel is a versatile material with advantages such as corrosion resistance and high temperature oxidation resistance. It is widely used in aviation, aerospace, shipbuilding, chemical industry, medical and other fields.