Sheet Metal Fabraction Process Route
Sheet metal is widely used in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, construction, home appliances, etc. The main steps of sheet metal process include shearing, punching/cutting, and folding. Among them, shearing is to cut the material to the required size; stamping is to use a mold to plastically deform the material to achieve the required shape and size; bending is to bend the material to the required angle. In addition, the sheet metal process also requires the use of various auxiliary equipment, such as uncoilers, leveling machines, deburring machines, spot welding machines, etc.
Sheet metal process route:
In order to ensure the consistency of the quality of the parts, Ruiyi strictly requires the following part processing process route: analyze the drawings and models, confirm the processing technology → → blanking (laser, CNC punching or other forms) → → deburring → → forming (bending) and stamping)→→Welding and grinding-→Cleaning--Packaging→Transportation.
The sheet metal process flow includes the following main steps:
1. Raw material preparation: Select suitable sheet metal materials, such as steel plates, aluminum plates, iron plates, etc., and cut them according to product requirements to obtain the required raw material dimensions.
2. Proofing and design: Make samples of sheet metal parts according to product requirements and design drawings. Confirm the accuracy and feasibility of the design through samples.
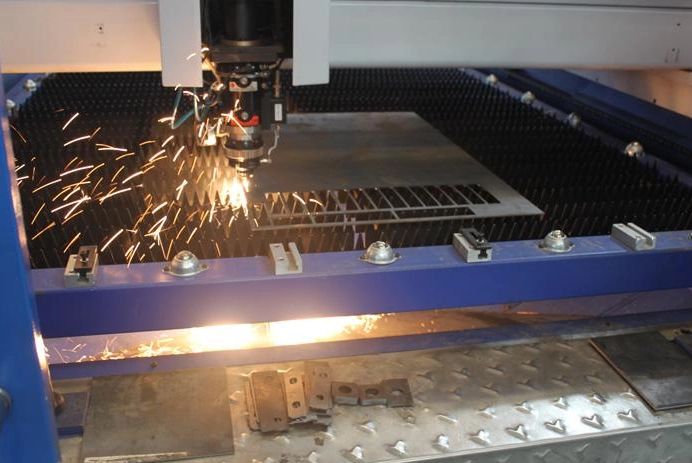
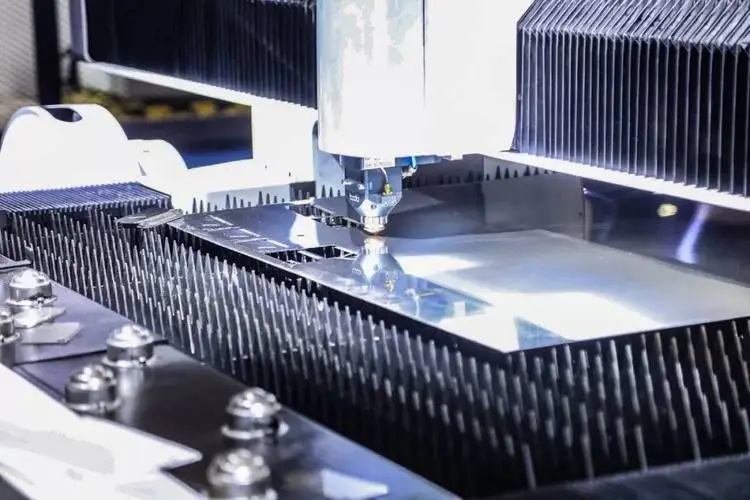
3. CNC Cutting: Use computer-aided programming (CAM) software to convert the design drawing into machine-readable code, and use a CNC cutting machine to perform cutting, trimming or punching operations to cut the sheet into the required shape. Laser cutting machines or punch machines process materials according to programming files. Laser cutting machines can meet the needs of cutting parts of various shapes, and punch machines have advantages in batch processing.

4. Deburring: Use grinders, files and other tools to remove the burrs on the surface of the workpiece to make the workpiece smooth and flat to prevent cuts and scratches.
5. Bending and forming: According to the dimensions marked on the bending diagram, use a bending machine to bend and shape the workpiece to obtain the required outline and angle. Bending molds are divided into upper molds and lower molds. Different shapes require different molds. The quality of the molds determines the accuracy of the bending dimensions. Molds are used on ordinary punch machines or other equipment to directly change the workpiece into the desired shape. Most of them are stamping forming, which is widely used in the fields of automotive sheet metal and electronic products.

6. Punching and tapping: Use a punch or laser cutting machine to punch or drill holes to form connecting holes, positioning holes or assembly holes for components. According to the bottom hole of the workpiece, the corresponding internal thread is processed on the workpiece. Tapping has requirements on the thickness of the plate - if it is too thin, it will easily slip.

7. Counterbore: A tapered hole is processed on the workpiece. In order to have a good appearance during the installation process, the workpiece is often installed with a countersunk hole without exposed screw heads.

8. Pressure riveting: Use a punch or hydraulic press to firmly press fasteners such as riveting nuts, riveting screws or riveting nut columns onto the workpiece. Pressure riveting requires pre-drilling a bottom hole on the workpiece. During bending Pressing the fastener onto the workpiece first can reduce the welding workload and protect the appearance of special workpieces.
9. Riveting: Pre-drill bottom holes on the workpiece, and use a rivet gun and rivets to tightly connect two or more workpieces together. It has good hole filling performance, good air tightness, and high riveting strength.
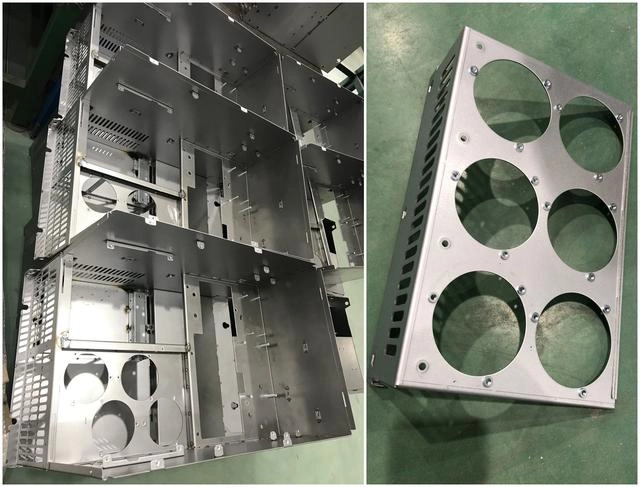
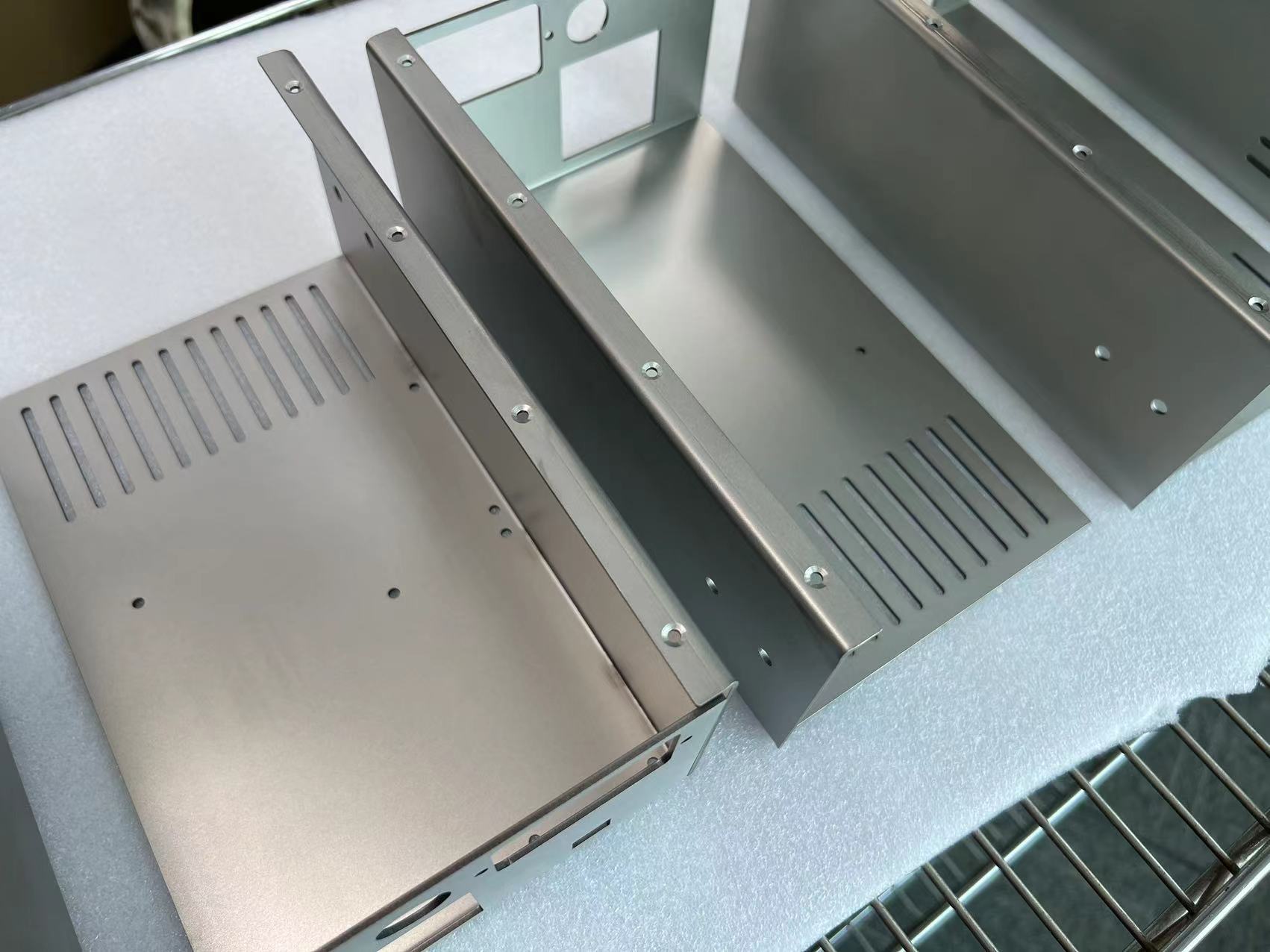
10. Welding and assembly: According to product requirements, use welding equipment to weld or assemble sheet metal parts to form a complete sheet metal product.
11. Surface treatment: Surface treatment is performed on sheet metal products, such as spraying, electrophoretic coating, anodizing, brushed, etc., to improve appearance and corrosion resistance.
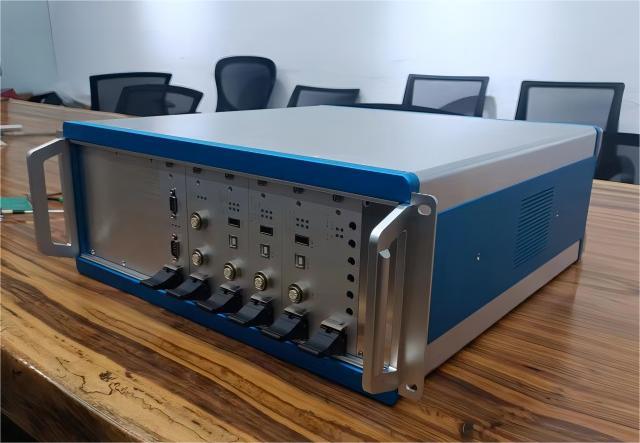

12. Inspection and quality control: Inspect the processed sheet metal products to ensure that the dimensions, surface quality, assembly accuracy, etc. meet the requirements. Make necessary corrections and adjustments.
13. Packaging and Shipping: Properly package the completed sheet metal products to prevent damage and arrange suitable transportation methods for shipment.

The sheet metal process flow can be adjusted according to the requirements and complexity of the specific product. The above steps provide a general sheet metal processing process framework. In actual operation, the process needs to be flexibly adjusted and organized according to specific situations and requirements.



